# Linux - Internet Checker Script V1.0
# Function to check network interface
check_interface()
local INTERFACE=$(ip route | grep default | awk '{print $5}')
if [[ -n "$INTERFACE" ]]; then
echo -e "\e[32mNetwork interface ($INTERFACE) is up.\e[0m"
else
echo -e "\e[31mNo network interface found or it is down!\e[0m"
return 1
fi
}
# Function to check default gateway
check_gateway() {
local GATEWAY=$(ip route | grep default | awk '{print $3}')
if ping -c 2 "$GATEWAY" &> /dev/null; then
echo -e "\e[32mSuccessfully connected to gateway ($GATEWAY).\e[0m"
else
echo -e "\e[31mFailed to connect to the gateway ($GATEWAY).\e[0m"
return 1
fi
}
# Function to check DNS resolution
check_dns() {
if nslookup google.com &> /dev/null; then
echo -e "\e[32mDNS resolution is working.\e[0m"
else
echo -e "\e[31mDNS resolution failed!\e[0m"
return 1
fi
}
# Function to check connectivity to external servers via ping
check_ping() {
local SERVERS=("8.8.8.8" "1.1.1.1" "google.com")
for server in "${SERVERS[@]}"; do
if ping -c 2 "$server" &> /dev/null; then
echo -e "\e[32mSuccessfully pinged $server.\e[0m"
else
echo -e "\e[31mFailed to ping $server.\e[0m"
return 1
fi
done
}
# Function to check if specific ports are open
check_ports() {
local PORTS=(80 443)
for port in "${PORTS[@]}"; do
if nc -zv google.com $port &> /dev/null; then
echo -e "\e[32mPort $port is accessible.\e[0m"
else
echo -e "\e[31mPort $port is not accessible!\e[0m"
return 1
fi
done
}
# Function to check traceroute to Google DNS
check_traceroute() {
if command -v traceroute &> /dev/null; then
echo -e "\e[32mTraceroute to Google DNS (8.8.8.8) is possible:\e[0m"
traceroute -m 5 8.8.8.8
else
echo -e "\e[31mTraceroute command not available on this system.\e[0m"
fi
}
# Function to check HTTP request and handle redirects
check_http_request() {
if curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" https://google.com | grep -q "200\|301\|302"; then
echo -e "\e[32mHTTP request successful or redirected.\e[0m"
else
echo -e "\e[31mHTTP request failed!\e[0m"
return 1
fi
}
# Run all checks
echo "Starting detailed internet connection check..."
check_interface
check_gateway
check_dns
check_ping
check_ports
check_traceroute
check_http_request
echo "Internet connection check complete."
Author: bytesmith17
I’m a tech enthusiast who’s been passionate about technology since I got my first PC at 11. For the past 20+ years, ICT has been both my career and hobby. I studied ICT, Business, and Photography at college before landing my first IT role in 2010, supporting a small software development company’s users. Since then, I’ve transitioned into the public sector as a network and telephony engineer. Today, I manage a mix of Cisco Call Manager, Avaya CS1K, and more as we plan to migrate to Teams.
run the following command
nano /fail2ban.sh
Copy and paste the script below.
#!/bin/bash
# Fail2Ban auto-install and setup script (no sudo)
# Step 1: Update package list and install Fail2Ban and rsyslog
apt update && apt install fail2ban rsyslog -y
# Step 2: Ensure rsyslog is running and enabled on boot
systemctl start rsyslog
systemctl enable rsyslog
# Step 3: Configure rsyslog to log auth messages
if ! grep -q "^auth,authpriv.*" /etc/rsyslog.conf; then
echo "auth,authpriv.* /var/log/auth.log" >> /etc/rsyslog.conf
echo "Configured rsyslog to log authentication messages."
fi
# Restart rsyslog to apply changes
systemctl restart rsyslog
# Step 4: Copy the default jail.conf to jail.local to prevent overwriting in updates
cp /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
# Step 5: Configure the SSH jail and other settings in jail.local
if ! grep -q "^\[DEFAULT\]" /etc/fail2ban/jail.local; then
echo -e "\n[DEFAULT]\n" >> /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
fi
# Check and set bantime if it doesn't exist
if ! grep -q "^bantime" /etc/fail2ban/jail.local; then
echo "bantime = 24h" >> /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
else
sed -i 's/^bantime.*/bantime = 24h/' /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
fi
# Check and set findtime if it doesn't exist
if ! grep -q "^findtime" /etc/fail2ban/jail.local; then
echo "findtime = 10m" >> /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
else
sed -i 's/^findtime.*/findtime = 10m/' /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
fi
# Check and set maxretry if it doesn't exist
if ! grep -q "^maxretry" /etc/fail2ban/jail.local; then
echo "maxretry = 5" >> /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
else
sed -i 's/^maxretry.*/maxretry = 5/' /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
fi
# Configure the SSH jail
if ! grep -q "^\[sshd\]" /etc/fail2ban/jail.local; then
echo -e "\n[sshd]\nenabled = true\nlogpath = /var/log/auth.log\n" >> /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
else
sed -i 's/^enabled.*/enabled = true/' /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
sed -i 's|^logpath.*|logpath = /var/log/auth.log|' /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
fi
# Step 6: Ensure SSH logging is enabled in /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# Handle LogLevel
if grep -q "^#LogLevel" /etc/ssh/sshd_config; then
sed -i 's/^#LogLevel.*/LogLevel INFO/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
elif grep -q "^LogLevel" /etc/ssh/sshd_config; then
sed -i 's/^LogLevel.*/LogLevel INFO/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
else
echo "LogLevel INFO" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
fi
# Handle SyslogFacility
if grep -q "^#SyslogFacility" /etc/ssh/sshd_config; then
sed -i 's/^#SyslogFacility.*/SyslogFacility AUTH/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
elif grep -q "^SyslogFacility" /etc/ssh/sshd_config; then
sed -i 's/^SyslogFacility.*/SyslogFacility AUTH/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
else
echo "SyslogFacility AUTH" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
fi
# Step 7: Restart SSH and Fail2Ban services to apply the changes
systemctl restart sshd
systemctl restart fail2ban
# Step 8: Enable Fail2Ban on boot
systemctl enable fail2ban
echo "Fail2Ban and rsyslog have been installed and configured successfully."
CTRL + O Then CTRL + X to Save and Close the file.
Now run the following command to sent the scripts permissions
chmod 755 /fail2ban.sh
Now we need to run the script to automatically install and setup fail2ban
./fail2ban.sh
Step 1 – Stop The Emby-Server Service
systemctl stop emby-server
Step 2 – Check The Emby-Server Service have safely stopped
systemctl status emby-server
important – ensure the emby server has stopped and shows inactive (dead)
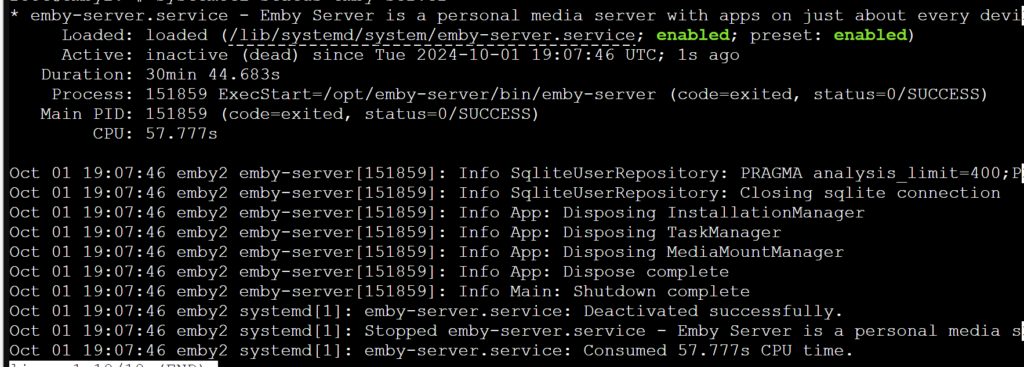
Step 3 – Amend the emby server service files
nano /usr/lib/systemd/system/emby-server.service
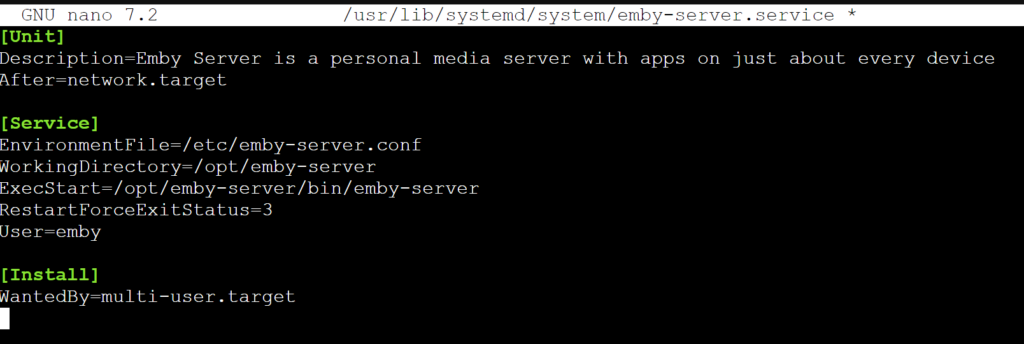
important – Replace “newuser” with the user you would like to use.
Change ‘User=emby’ to ‘User=newuser’
Save emby-server.service CTRL + O then Enter
Step 4 – change emby folder’s permissionchown -R newuser:newuser /var/lib/emby/
Step 5 – reload and check the emby server service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
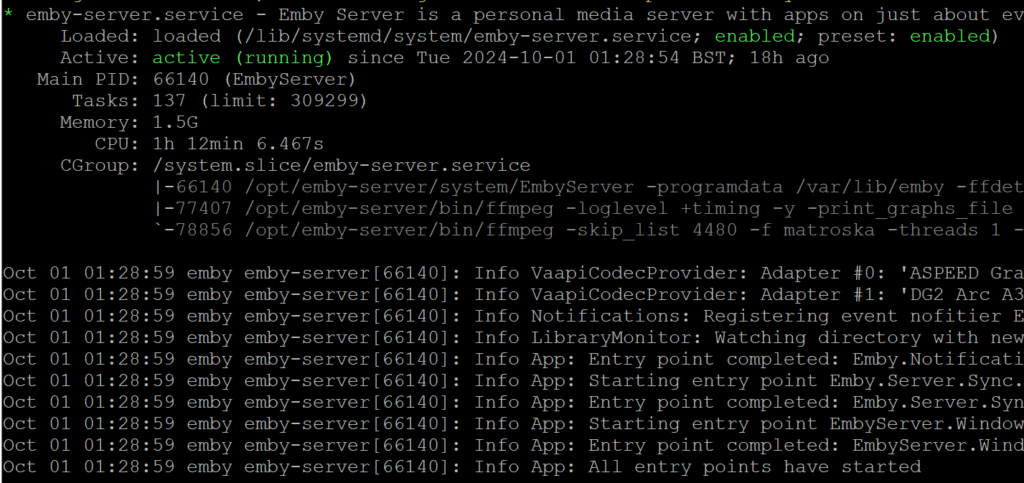
systemctl start emby-serversystemctl status emby-server
Checking the status of emby you should see active (Running) shown in green below.
Important: This is for use with Debian 12 (BookWorm) / Proxmox (8.2.7).
This guide is for the setup of an Intel iGPU or dedicated GPU passthrough on Proxmox between an LXC / CT linux system.
Run these commands on both the proxmox host and Emby CT. I have this method working on successfully on both a N100 iGPU and Sparkle Intel Arc A310 ECO
Step 1 – Adding driver download sources nano /etc/apt/sources.list
add the following
non-free firmwares
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm non-free-firmware
non-free drivers and components
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm non-free
Step 2 – Installing the GPU Driver
Install the followingapt update && apt install intel-media-va-driver-non-free intel-gpu-tools
Step 3 – Confirm GPU’s major number’s for fb0 and renderD128
Important: Note down your major numbers from your output my example numbers may not be the same as yours and if this are incorrect the gpu will not work.
cd /dev
Use the following command to list all files and folders in the current directory
ls -lah
Make a note of the numbers in bold for fb0 (If it exists)
crw-rw---- 1 root video 29, 0 Aug 30 21:19 fb0
Navigate to the dri folder using the following command
cd /dev/dri
ls -lah
Make a note of the the number in bold for renderD128
crwxrwxrwx 1 root render 226, 128 Aug 30 21:19 renderD128
Step 4 – Amend Proxmox CT/LXC config to allow access to the GPU
Now we will add the numbers that were noted down to our CT config on proxmox for Emby – Important amend the command below with your CT’s ID number shown the proxmox webgui (Example Below) Mine is 3006

Now open your CT’s config files on your Proxmox host.
nano /etc/pve/lxc/3006.conf
Add the following lines to the file and save using CTRL + O and then enter.lxc.cgroup2.devices.allow: c 29:* rwm
lxc.cgroup2.devices.allow: c 226:* rwm
lxc.mount.entry: /dev/fb0 dev/fb0 none bind,optional,create=file
lxc.mount.entry: /dev/dri dev/dri none bind,optional,create=dir
lxc.apparmor.profile: unconfined
Step 5 – Adding Persistent GPU Permissions
Important: Giving 777 permissions to your GPU is not considered best practice from a security standpoint. While this approach works, there are more secure methods you can follow. However, I understand the risks and accept them on my system. do this at your own risk…
Adding Persistent GPU Permissions on proxmox host so the GPU is accessible to the CT after reboot.
nano /etc/udev/rules.d/99-renderD128-permissions.rules
KERNEL=="renderD128", MODE="0777"
udevadm control --reload-rules
udevadm trigger
How to Test?
Run the following command on your proxmox shell (This is basically task manager for your GPU)
intel_gpu_top
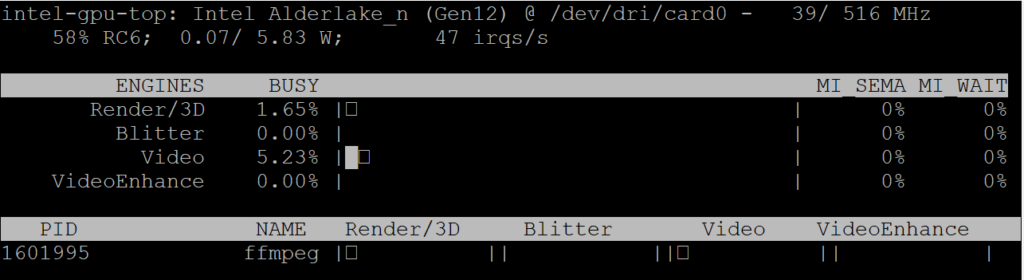
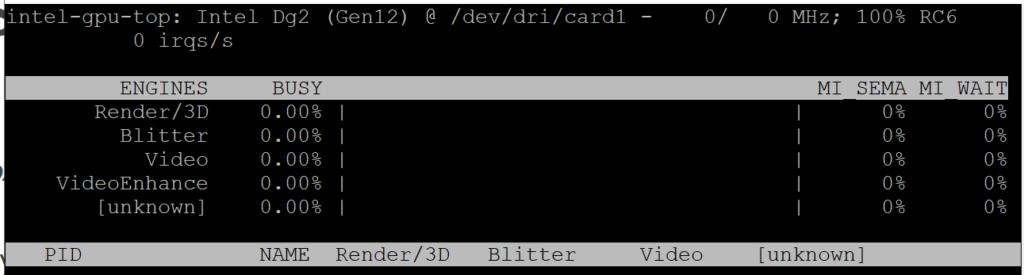
Step 6 – LXC/CT GPU Driver installation
Repeat Steps 1 and 2 inside your LXC/CT/Emby Shell
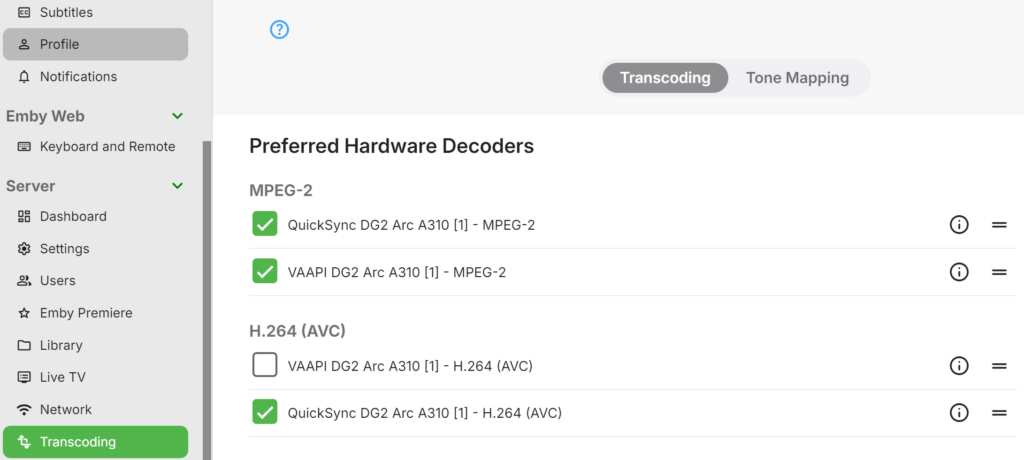
How to Test GPU in Emby?
Login to Emby and navigate on the admin webpage to Server > Transcoding. If you see your GPU and a list of Hardware Decoders its likely working. Test forcing something to Trancode by changing the bitrate and monitor the CPU usage and using intel_gpu_top to see if there is any ffmpeg processes running on the GPU
If your not seeing anything on this page I suggest giving your server a little nap (aka, a reboot) see if that makes the GPU driver jumps into life.
Important: Giving 777 permissions to your GPU is not considered best practice from a security standpoint. While this approach works, there are more secure methods you can follow. However, I understand the risks and accept them on my system. do this at your own risk…
If you are having issues with GPU transcoding in emby and your GPU permission keep changing after reboot use the following commands to fix the permission.
Run the following command inside your proxmox shell.
nano /etc/udev/rules.d/99-renderD128-permissions.rules
Add the following to the file
KERNEL=="renderD128", MODE="0777"
CTRL + O then Enter to save the changes to the file.
Now run the following command
udevadm control --reload-rules
Run the following command
udevadm trigger